Introduction to prenol
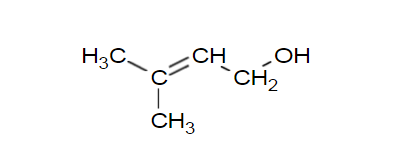
Prenol, also known as 3-methyl-2-butene-1-ol, English name 3-Methyl-2-buten-1-ol, relative molecular mass 86.13, boiling point 140 ° C, density 0.848 g / mL ( 25 ° C), vapor pressure 1.4 mm Hg (20 ° C), is a colorless transparent liquid. Its structural formula is as shown:
Prenol is mainly used for the synthesis of methyl guanidine, which is an intermediate of high-efficiency and low-toxic pyrethroid insecticides. With the continuous improvement of the process for synthesizing prenyl alcohol, the research and development has been deepened, and its application in pesticide production is also expanding, and the market demand has increased significantly. Methyl phenate is an important precursor of pyrethroids. Usually, trimethyl orthoacetate and prenol are condensed and rearranged in the presence of an acidic catalyst to form methyl guanidine. Pyrethroid insecticides have a strong contact effect on most pests, their vapors can also drive off pests, and they are less toxic to mammals and birds. It is environmentally friendly due to its ease of degradation. Therefore, it is suitable for a variety of public health places. Prenyl alcohol is also the main intermediate of TPEG, a raw material for the production of polycarboxylate water-reducing agents. The use of this high-performance cement water reducer in the production and construction of concrete can reduce the water consumption by more than 30%, increase the strength of concrete by more than 30%, and reduce the amount of cement under the same conditions.